① Microarray system for onsite diagnoses
We have developed a new microarray preparation method using new special photo-reactive polymers. The microarray chips have covalently immobilized biopolymers, virus components, or cells and also provide high S/N ratio because of suppressing nonspecific protein adsorption on non-immobilized regions. In addition, we have developed an instrument that can automatically assay the interactions of molecules with the microarray-immobilized ones.
The world’s first compact microarray measurement platform was realized as DropScreen® which is commercially available from Nippon Chemiphar Co., Ltd. in Japan. The allergy detection kit is approved as an in vitro diagnostic and covered by Japanese Medical Insurance.

<Related Publications>
Microarray for COVID-19 antibody detection
- J. Akimoto, et al., “Rapid and quantitative detection of multiple antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 mutant proteins by photo-immobilized microarray”, Anal. Sci., 38, 1313 (2022)
- H. Kashiwagi, et al., “SARS-CoV-2 proteins microarray by photoimmobilization for serodiagnosis of the antibodies”, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 94, 2435 (2021)
Microarray for allergy diagnosis (specific IgE for allergen)
- P. M. Sivakumar, et al., “Novel microarrays for simultaneous serodiagnosis of multiple antiviral antibodies”, PLoS ONE, 8, e81726 (2013)
Microarray for infection history
- Ponnurengam Malliappan Sivakumar, Nozomi Moritsugu, Sei Obuse, Takashi Isoshima, Hideo Tashiro, and Yoshihiro Ito, “Novel microarrays for simultaneous serodiagnosis of multiple antiviral antibodies”, PLoS ONE, 8, e81726 (2013)
Microarray for auto-immune diseases diagnosis
- T. Matsudaira, et al., “Automated microfluidic assay system for autoantibodies found in autoimmune diseases using a photoimmobilized autoantigen microarray,” Biotechnol. Prog., 24, 1384 (2008)
Microarray of cells for antibody typing
- Y. Ito, et al., “Photo-immobilized array of panel cells for assay of antibodies”, Biomaterials, 27, 2502 (2006)
Photo-immobilization microarray
- Y. Ito, “Photoimmobilization for microarrays”, Biotechnol. Prog., 22, 924 (2006)
② Biofunctional materials and stimli-responsive materials
We have developed various polymeric materials for preparation of functional surfaces on various materials including organic and inorganic ones. For example, it is possible to make any common materials non-specific binding-suppressive or biological active. Photo- and thermos-responsive polymers have been also developed.

<Related Publications>
- Kun Fang, et al., “Cyclic stretch modulates cell morphology transition under geometrical confinement by covalently immobilized gelatin”, J. Mater. Chem. B, 11, 9155 (2023)
- M. H. M. Othman, et al., “Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol-grafted photoreactive polyethylene glycols for antibiofouling applications”, Polymers, 15, 184 (2023)
- S. Tada, et al., “Versatile mitogenic and differentiation-inducible layer formation by underwater adhesive polypeptides”, Adv. Sci., 2100961 (2021)
- J. Akimoto, et al., “Synthesis of photoreactive poly(ethylene oxide)s for surface modification”, ACS Appl. Bio Mater., 3, 5941 (2020)
- Y. Heo, et al., “Gelation and release behavior of visible light-curable alginate”, Polym. J., 52, 323 (2020)
- H. Mao, et al., “Serum-free culturing of human mesenchymal stem cells with immobilized growth factors”, J. Mater. Chem. B, 5, 928 (2017)
- T. Ishii, et al., “A new nonbiofouling polyzwitterion including L-histidine”, Biomacromolecules, 8, 3340 (2007)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Surface modification of plastic, glass and titanium by photoimmobilization of polyethylene glycol for antibiofouling”, Acta Biomater., 3, 1024 (2007)
- T. Konno, et al., “Culture of mouse embryonic stem cells on photoimmobilized polymers”, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 102, 304 (2006)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Photoimmobilized array of panel cells for assay of antibodies”, Biomaterials, 27, 2502 (2006)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Photo-reactive polyvinylalcohol for photo-immobilized microarray”, Biomaterials, 26, 211 (2005)
- T. Konno, et al., “Photo-immobilization of a phospholipids polymer”, Biomaterials, 26, 1381 (2005)
- H. Hasuda, et al., “Synthesis of photoreactive pullulan for surface modification”, Biomaterials, 26, 2401 (2005)
③ Drug discovery by molecular evolutionary engineering
Molecular library composed of low-molecular weight compounds (drugs) and random sequences of peptide has been developed for therapeutic and diagnostic drug discovery.
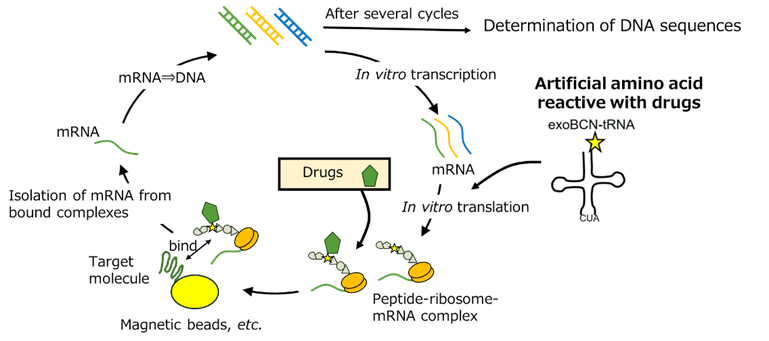
<Related Publications>
- D. P. Tran, et al., “Using molecular dynamics simulations to prioritize and understand AI-generated cell penetrating peptides”, Sci. Rep., 11, 10630 (2021)
- S.-W. Kim, et al., “Selection of ovalbumin-specific binding peptides through instant translation in ribosome display using E.coli extract”, Anal. Sci., 37, 707 (2021)
- C. Phadke, et al., “Instantaneous detection of α-casein in cow’s milk using fluorogenic peptide aptamers”, Anal. Methods, 12, 1368 (2020)
- K. C. T. Bahadur, et al., “In vitro selection of electrochemical peptide probes using bioorthogonal tRNA for influenza virus detection”, Chem. Commun., 54, 5201 (2018)
- K. C. T. Bahadur, et al., “Wash-free and selective imaging of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) expressing cells with fluorogenic peptide ligands”, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 500, 283(2018)
- W. Wang, et al., “Fluorogenic enhancement of in vitro selected binding peptide ligand by replacement of fluorescent group”, Anal. Chem., 88, 7991 (2016)
- W. Wang, et al., “Assisted enhancement of inhibitory effects of small molecular inhibitors for kinases”, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 89, 444-446 (2016)
- W. Wang, et al., “In vitro selection of a peptide aptamer that potentiates inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by purvalanol”, Med. Chem. Commun., 5, 1400 (2014)
- W. Wang, et al., “A fluorogenic peptide probe developed by in vitro selection using tRNA carrying a fluorogenic amino acid”, Chem Commun., 50, 2962 (2014)
- W. Wang, et al., “Polypeptide aptamer selection using a stabilized ribosome display”, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 112, 515 (2011)
④ Drug discovery from library composed of low molecular weight compounds-random sequence of peptide conjugates
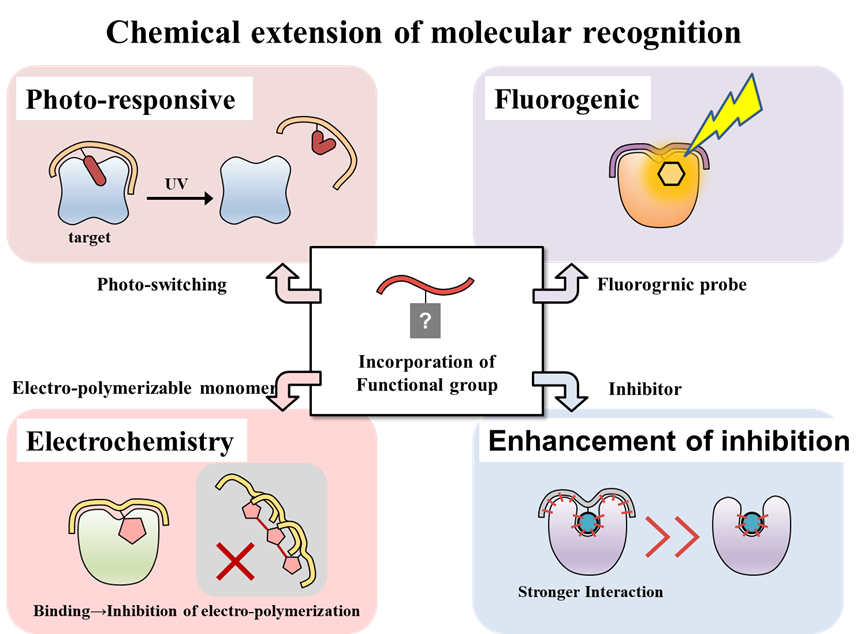
The molecular evolution engineering developed by RIKEN has produced various functional peptide aptamers. Here peptides assisted activity and selectivity of low molecular weight drugs are aimed. Repositioning of low molecular weight drugs, replacement of antibody, middle molecular weight of drugs, and solid-phase synthesis will be enabled.
