関連書籍
- 伊藤嘉浩著「バイオ医用高分子」日本化学会編、共立出版 (2023)
- Yoshihiro Ito, ed. “Photochemistry for Biomedical Applications”, Springer-Nature (2018)
- 伊藤嘉浩監修「バイオチップの基礎と応用」CMC出版 (2015)
- 伊藤嘉浩監修「マイクロアレイ・バイオチップの最新技術」CMC出版 (2007)
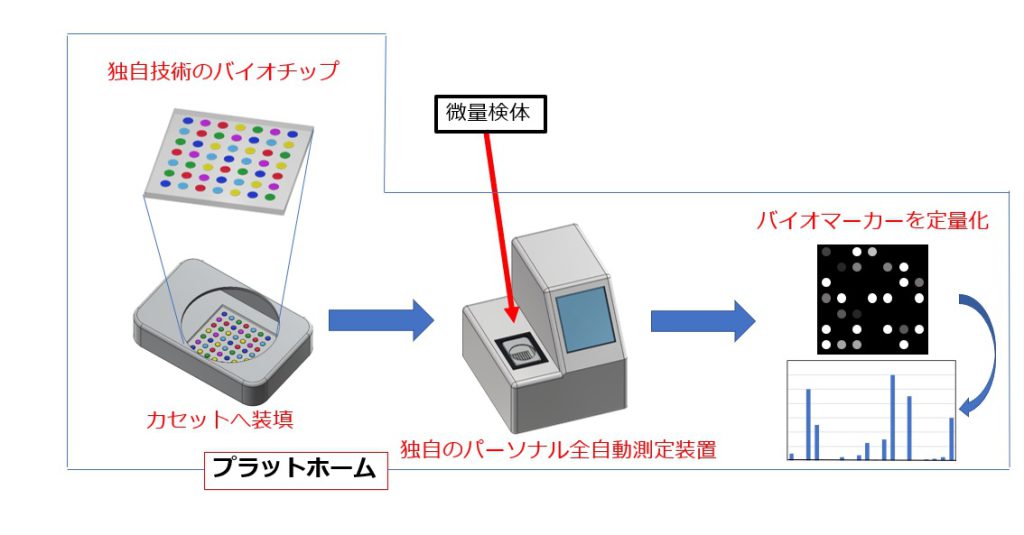
① タンパク質マイクロアレイ・バイオチップを用いた多項目分析
多様なタンパク質をはじめとする生体高分子や有機分子を1枚の基板の上に共有結合固定化し、しかも非特異的なタンパク質吸着を抑制することで高S/N比を実現しました。そして完全自動化して測定できる装置も開発し、世界初の小型マイクロアレイ・バイオチップ測定プラットホームを実現し、医療応用できるレベルまでにしました。
- Akimoto, et al., “Rapid and quantitative detection of multiple antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 mutant proteins by photo-immobilized microarray”, Anal. Sci., 38, 1313 (2022)
- H. Kashiwagi, et al., “SARS-CoV-2 proteins microarray by photoimmobilization for serodiagnosis of the antibodies”, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 94, 2435 (2021)
- P. M. Sivakumar, et al., “Novel microarrays for simultaneous serodiagnosis of multiple antiviral antibodies”, PLoS ONE, 8, e81726 (2013)
- Ito, et al., “An automated multiplex specific IgE assay system using a photoimmobilized microarray”, J. Biotechnol., 161, 414 (2012)
- S. Tsuzuki, et al., “Photo-immobilization of biological components on gold-coated chips for measurements using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM)”, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 102, 700 (2009)
- Matsudaira, et al., “Automated microfluidic assay system for autoantibodies found in autoimmune diseases using a photoimmobilized autoantigen microarray”, Biotechnol. Prog., 24, 1384 (2008)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Photo-immobilized array of panel cells for assay of antibodies”, Biomaterials, 27, 2502 (2006)
- Y. Ito, “Photoimmobilization for microarrays”, Biotechnol. Prog., 22, 924 (2006)
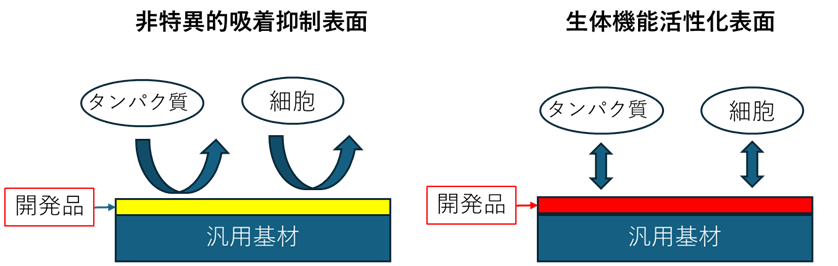
② 刺激応答性高分子技術
開発した高分子材料によって、様々な生体高分子を無機・有機材料表面に固定化して機能化できるようにします。例えば、任意の汎用基材に生体(細胞)活性化表面を創出することが可能です。光や熱に応答する新しい高分子の技術を開発しました。
- Kun Fang, et al., “Cyclic stretch modulates cell morphology transition under geometrical confinement by covalently immobilized gelatin”, J. Mater. Chem. B, 11, 9155 (2023)
- M. H. M. Othman, et al., “Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol-grafted photoreactive polyethylene glycols for antibiofouling applications”, Polymers, 15, 184 (2023)
- S. Tada, et al., “Versatile mitogenic and differentiation-inducible layer formation by underwater adhesive polypeptides”, Adv. Sci., 2100961 (2021)
- J. Akimoto, et al., “Synthesis of photoreactive poly(ethylene oxide)s for surface modification”, ACS Appl. Bio Mater., 3, 5941 (2020)
- Y. Heo, et al., “Gelation and release behavior of visible light-curable alginate”, Polym. J., 52, 323 (2020)
- H. Mao, et al., “Serum-free culturing of human mesenchymal stem cells with immobilized growth factors”, J. Mater. Chem. B, 5, 928 (2017)
- T. Ishii, et al., “A new nonbiofouling polyzwitterion including L-histidine”, Biomacromolecules, 8, 3340 (2007)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Surface modification of plastic, glass and titanium by photoimmobilization of polyethylene glycol for antibiofouling”, Acta Biomater., 3, 1024 (2007)
- T. Konno, et al., “Culture of mouse embryonic stem cells on photoimmobilized polymers”, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 102, 304 (2006)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Photoimmobilized array of panel cells for assay of antibodies”, Biomaterials, 27, 2502 (2006)
- Y. Ito, et al., “Photo-reactive polyvinylalcohol for photo-immobilized microarray”, Biomaterials, 26, 211 (2005)
- T. Konno, et al., “Photo-immobilization of a phospholipids polymer”, Biomaterials, 26, 1381 (2005)
- H. Hasuda, et al., “Synthesis of photoreactive pullulan for surface modification”, Biomaterials, 26, 2401 (2005)
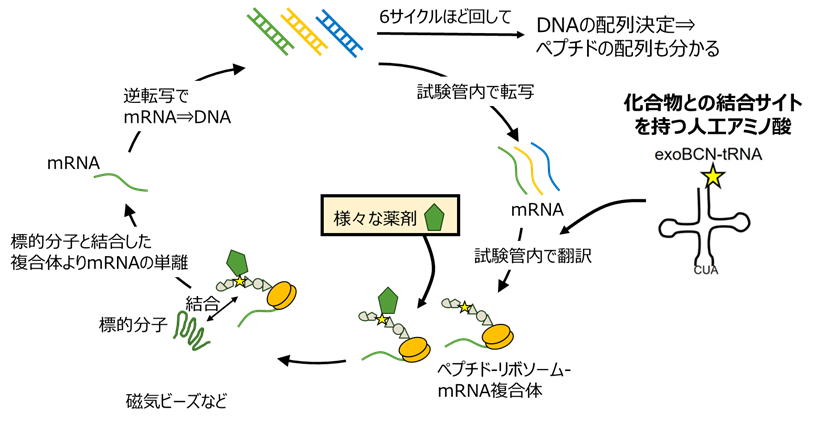
③ 進化分子工学による新たな分子認識素子の創成
非天然アミノ酸を組み込んだ新しい分子認識素子を開発できる進化分子工学を開発し、診断薬や治療薬への応用展開を目指しています。
- D. P. Tran, et al., “Using molecular dynamics simulations to prioritize and understand AI-generated cell penetrating peptides”, Sci. Rep., 11, 10630 (2021)
- S.-W. Kim, et al., “Selection of ovalbumin-specific binding peptides through instant translation in ribosome display using E.coli extract”, Anal. Sci., 37, 707 (2021)
- C. Phadke, et al., “Instantaneous detection of α-casein in cow’s milk using fluorogenic peptide aptamers”, Anal. Methods, 12, 1368 (2020)
- K. C. T. Bahadur, et al., “In vitro selection of electrochemical peptide probes using bioorthogonal tRNA for influenza virus detection”, Chem. Commun., 54, 5201 (2018)
- K. C. T. Bahadur, et al., “Wash-free and selective imaging of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) expressing cells with fluorogenic peptide ligands”, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 500, 283(2018)
- W. Wang, et al., “Fluorogenic enhancement of in vitro selected binding peptide ligand by replacement of fluorescent group”, Anal. Chem., 88, 7991 (2016)
- W. Wang, et al., “Assisted enhancement of inhibitory effects of small molecular inhibitors for kinases”, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 89, 444-446 (2016)
- W. Wang, et al., “In vitro selection of a peptide aptamer that potentiates inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by purvalanol”, Med. Chem. Commun., 5, 1400 (2014)
- W. Wang, et al., “A fluorogenic peptide probe developed by in vitro selection using tRNA carrying a fluorogenic amino acid”, Chem Commun., 50, 2962 (2014)
- W. Wang, et al., “Polypeptide aptamer selection using a stabilized ribosome display”, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 112, 515 (2011)
